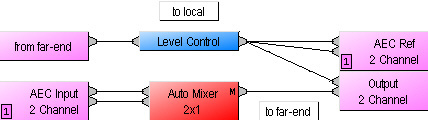
AEC Inputs provide acoustic echo cancellation and background noise reduction, and are available in pairs only as part of AudiaFLEX hardware.
NOTE: Newer AEC-2HD input cards have a wider bandwidth (20kHz) than earlier AEC2 input cards (7kHz). For proper performance, AEC Inputs must be used in conjunction with Auto Mixer blocks. When placed into the Layout, AEC Inputs consist of two separate blocks. An AEC Input block represents the actual audio inputs, and an AEC Ref block provides the associated signal reference points. In conferencing applications, AEC Ref blocks should receive 'far-end' signal only, and be connected as close as possible to the output, so as to include any signal level adjustments applied for local sound reinforcement of that signal. This approach provides the most accurate reference. AEC Ref blocks should never be connected to paths containing signal from corresponding AEC Inputs.

In applications where only background noise reduction is desired, AEC can be turned off and no AEC Ref connection is required. Noise Reduction is intended for 'stationary' or steady-state background noises, such as from HVAC systems, fans, motors, or other mechanical devices.
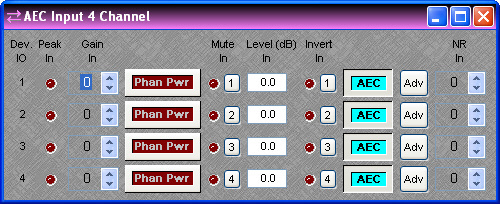
Device IO indicates which hardware input is associated with that software channel. Gain In compensates for different input levels (mic or line), and should be set so Peak In flashes only occasionally (6dB headroom). Phan Pwr assigns +48 Volt phantom power to the input for condenser microphones. Mute In turns the input signal on/off. Level In adjusts the relative input volume. Invert In reverses the polarity of the input signal. AEC turns on/off acoustic echo cancellation. Adv opens an Advanced dialog. NR In selects the amount of background noise reduction to be applied (6~15dB).
|
Each channel of AEC has an Advanced dialog box. ERL (Echo Return Loss) shows the level difference between a signal at the speaker output (AEC Ref) and that same signal as picked up at the mic (AEC Input). ERLE (Echo Return Loss Enhancement) indicates the amount of processing being applied on that channel. TER (Total Echo Reduction) shows the combined echo reduction achieved by acoustic damping (ERL) and signal processing (ERLE). Nonlinear Processing provides additional echo cancellation, for more challenging applications. However, increased Nonlinear Processing can also adversely affect full-duplex operation. |
|
The Advanced dialog for newer AEC-2HD cards includes added features. Ref, Mic, and Out display levels at the AEC Ref block and at the AEC block (pre & post AEC respectively). Echo Detect indicates AEC in progress. Echo Path Changed indicates AEC converging. Min Threshold prevents AEC re-convergence due to momentarily low levels (such as muted mics). |